Boston
Astronomy
Welcome to the Boston Astronomy website ...
This website has been created by and is supported by a group of Boston, MA - area amateur astronomers. It is intended to be a convenient site to access news and information about astronomy and space-related activities of interest to the community and the public.
Range of Time in the Universe
This website has been created by and is supported by a group of Boston, MA - area amateur astronomers. It is intended to be a convenient site to access news and information about astronomy and space-related activities of interest to the community and the public.
Range of Time in the Universe
| Factor (s) | Multiple | Symbol | Definition | Comparative examples & common units | Orders of magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10−44 | 1 Planck time. | tP | The time required to travel one Planck length at the speed of light (c) | 5.4×10−20 ys
= 5.4×10−44 s:
One
Planck time tP =
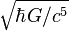 ≈ 5.4×10−44 s[2]
is the briefest physically meaningful span of time. It is the
unit of time in the
natural units system known as
Planck units.
≈ 5.4×10−44 s[2]
is the briefest physically meaningful span of time. It is the
unit of time in the
natural units system known as
Planck units. |
10−20 ys, 10−19 ys (10−44 s, 10−43 s) |
| 10−24 | 1 yoctosecond | ys[3] | Yoctosecond, (yocto- + second), is one septillionth of a second | 0.3 ys: mean life of the
W and Z bosons.[4][5][a] 0.5 ys: time for top quark decay, according to the Standard Model. 1 ys: time taken for a quark to emit a gluon. 23 ys: half-life of 7H. |
1 ys and less, 10 ys, 100 ys |
| 10−21 | 1 zeptosecond | zs | Zeptosecond, (zepto- + second), is one sextillionth of one second | 7 zs: half-life of
helium-9's outer neutron in the second
nuclear halo. 17 zs: approximate period of electromagnetic radiation at the boundary between gamma rays and X-rays. 300 zs: approximate typical cycle time of X-rays, on the boundary between hard and soft X-rays. 500 zs: current resolution of tools used to measure speed of chemical bonding[6] |
1 zs, 10 zs, 100 zs |
| 10−18 | 1 attosecond | as | One quintillionth of one second | 12 attoseconds: shortest measured period of time.[7] | 1 as, 10 as, 100 as |
| 10−15 | 1 femtosecond | fs | One quadrillionth of one second | 1 fs: Cycle time for 390 nanometre light; transition from visible light to ultraviolet; light travels 0.3 micrometers (µm) | 1 fs, 10 fs, 100 fs |
| 10−12 | 1 picosecond | ps | One trillionth of one second | 1 ps: half-life of a
bottom quark; light travels 0.3 millimeters (mm) 4 ps: Time to execute one machine cycle by an IBM Silicon-Germanium transistor |
1 ps, 10 ps, 100 ps |
| 10−9 | 1 nanosecond | ns | One billionth of one second | 1 ns: Time to execute one
machine cycle by a 1 GHz microprocessor 1 ns: Light travels 30 centimetres (12 in) |
1 ns, 10 ns, 100 ns |
| 10−6 | 1 microsecond | µs | One millionth of one second | 1 µs: Time to execute one
machine cycle by an Intel 80186 microprocessor 4–16 µs: Time to execute one machine cycle by a 1960s minicomputer |
1 µs, 10 µs, 100 µs |
| 10−3 | 1 millisecond | ms | One thousandth of one second | 1 ms: time for a neuron in human
brain to fire one impulse and return to rest[8] 4–8 ms: typical seek time for a computer hard disk 100–400 ms (=0.1–0.4 s): Blink of an eye[9] 18–300 ms (=0.02–0.3 s): Human reflex response to visual stimuli |
1 ms, 10 ms, 100 ms |
| 100 | 1 second | s |
1 s: 9,192,631,770 periods of the radiation
corresponding to the transition between the two hyperfine
levels of the ground state of the cesium-133 atom.[10]
60 s: 1 minute |
1 s, 10 s, 100 s | |
| 103 | 1
kilosecond (16.7 minutes) |
ks | One thousand seconds | 3.6 ks: 3600 s or 1 hour 86.4 ks: 86 400 s or 1 day 604.8 ks: 1 week |
103 s, 104 s, 105 s |
| 106 | 1
megasecond (11.6 days) |
Ms | One million seconds |
2.6 Ms: approximately 1 month |
106 s, 107 s, 108 s |
| 109 | 1
gigasecond (32 years) |
Gs | One billion seconds |
2.1 Gs: average
human
life expectancy at birth (2011 estimate)[11] |
109 s, 1010 s, 1011 s |
| 1012 | 1
terasecond (32 000 years) |
Ts | One trillion seconds |
6 Ts: time since the appearance of Homo sapiens (approximately) |
1012 s, 1013 s, 1014 s |
| 1015 | 1
petasecond (32 million years) |
Ps | One quadrillion seconds | 7.1–7.9 Ps: 1
galactic year (225-250 million years)[12] 143 Ps: the
age of the Earth[13][14][15] |
1015 s, 1016 s, 1017 s |
| 1018 | 1
exasecond (32 billion years) |
Es | One quintillion seconds | 312 Es: Estimated lifespan of a 0.1 solar mass red dwarf star. | 1018 s, 1019 s, 1020 s |
| 1021 | 1
zettasecond (32 trillion years) |
Zs | One sextillion seconds | 3 Zs: Estimated duration of Stelliferous Era. | 1021 s, 1022 s, 1023 s |
| 1024 | 1
yottasecond (32 quadrillion years) |
Ys | One septillion seconds | 1.6416 Ys: Estimated
half-life of the meta-stable
20983Bi radioactive isotope.
6.616×1050 Ys: Time required for a 1 solar mass black hole to evaporate completely due to Hawking radiation, if nothing more falls in. |
1024 s, 1025 s, 1026 s and more |
| Factor (a) | Multiple | Common units | Orders of magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10−50 | Planck time, the shortest physically meaningful interval of time ≈ 1.71×10−50 a | 10−50 a | |
| 10−24 | 1 yoctoannum | — | 1 ya and less, 10 ya, 100 ya |
| 10−21 | 1 zeptoannum | — | 1 za, 10 za, 100 za |
| 10−18 | 1 attoannum | — | 1 aa, 10 aa, 100 aa |
| 10−15 | 1 femtoannum | — | 1 fa, 10 fa, 100 fa |
| 10−12 | 1 picoannum | — | 1 pa, 10 pa, 100 pa |
| 10−9 | 1 nanoannum | 1 second = 3.17 × 10−8 a ≈ 10-7.50 a | 1 na, 10 na, 100 na |
| 10−6 | 1 microannum | 1 minute = 1.90 × 10−6 a 1 hour = 1.40 × 10−4 a |
1 ua, 10 ua, 100 ua |
| 10−3 | 1 milliannum | 1 day = 2.73 × 10−3 a 1 week = 1.91 × 10−2 a |
1 ma, 10 ma, 100 ma |
| 100 | 1 annum | 1 average year = 1 annum (= 365.24219
SI days) 1 decade = 10 a 1 century = 100 a |
1 a, 10 a, 100 a |
| 103 | 1 kiloannum | millennium = 1000 a | 103 a, 104 a, 105 a |
| 106 | 1 megaannum | epoch = 1,000,000 a | 106 a, 107 a, 108 a |
| 109 | 1 gigaannum | aeon = 1,000,000,000 a 13.8 Ga = 1.38×1010 a ≈ 13.8 billion years, the approximate age of the Universe |
109 a, 1010 a, 1011 a |
| 1012 | 1 teraannum | — | 1012 a, 1013 a, 1014 a |
| 1015 | 1 petaannum | — | 1015 a, 1016 a, 1017 a |
| 1018 | 1 exaannum | 19 exaannum, the estimated half-life of the "stable" 20983Bi radioactive isotope | 1018 a, 1019 a, 1020 a |
| 1021 | 1 zettaannum | — | 1021 a, 1022 a, 1023 a |
| 1024 | 1 yottaannum | — | 1024 a, 1025 a, 1026 and more |